fs::dir_ls("my_folder", regexp = ".*\\.shp$") %>%
purrr::map_dfr(sf::read_sf) This post is a mess. See the updated version.
dplyr::bind_rowsdoesn’t work on {sf} objectsbase::rbindneeds the objects to have the same structure and only works on two tables and so that’s not straightforward to use1.
→ So we’ll use purrr::map and tidyr::unnest.
NB : now in 2021, I advise to simply use:
or now in 2023, because map_dfr() is being superseded:
fs::dir_ls("my_folder", regexp = ".*\\.shp$") %>%
purrr::map(sf::read_sf) %>%
dplyr::bind_rows()dir_ls("my_folder", regexp = ".*\\.shp$") %>%
purrr::map(sf:::read_sf) %>%
purrr::list_rbind() %>%
sf::st_sf()As of October 2019 this method doesn’t work any longer, due to an update in the vctrs package.
https://github.com/r-spatial/sf/issues/1172.
So your best bet is to have the same structure in your shapefile and use:
dir_ls("shp", glob = "*.shp") %>%
map(read_sf) %>%
do.call(rbind, .)It works again with vctrs 0.2.2 (February 2020)
First get some data, the communes of three french départements:
library(tidyverse)
library(sf)
library(fs)
library(httr)
library(leaflet)
# https://fr.actualitix.com/blog/shapefiles-des-departements-de-france.html
url <- c("https://fr.actualitix.com/blog/actgeoshap/01-Ain.zip",
"https://fr.actualitix.com/blog/actgeoshap/73-savoie.zip",
"https://fr.actualitix.com/blog/actgeoshap/74-haute-savoie.zip")
dep <- str_extract(url, "\\d{2}.*$")
list(url, dep) %>%
pwalk(~ GET(.x, write_disk(.y)))
walk(dep, unzip, junkpaths = TRUE, exdir = "shp")We can then create a 3 rows data frame containing a list-column in which we store the sf object. Then we just unnest it. This operation erases the sf-class, we have to add it back.
res <- dir_ls("shp", glob = "*.shp") %>%
tibble(fname = .) %>%
mutate(data = map(fname, read_sf)) %>%
unnest(data) %>%
st_sf() %>%
st_set_crs("EPSG:2154")
write_sf(res, "shp/3dep.shp")
res %>%
st_transform(4326) %>%
leaflet() %>%
addPolygons() %>%
addTiles()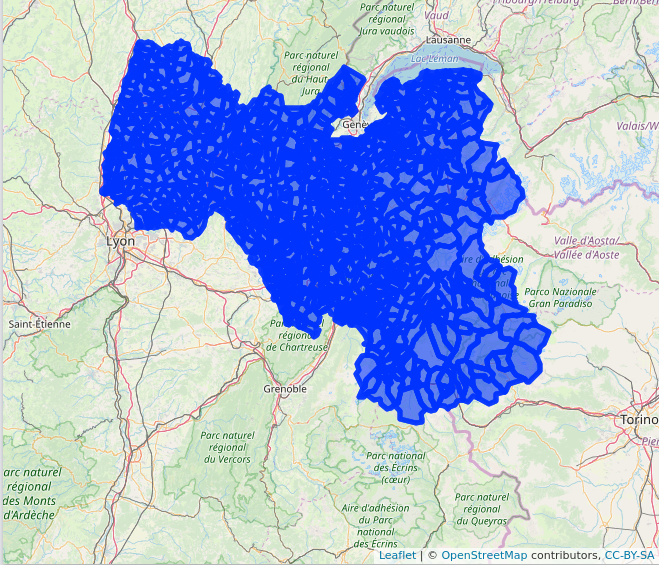
Bonus: we have the source filename stored in the resulting shapefile.
Footnotes
We could have used:
dir_ls("shp", glob = "*.shp") %>% map(read_sf) %\>% do.call(rbind, .)but the column structure doesn’t match here…↩︎